In “The Wonderful Mother of Oz,” Wagner argues that Baum infused his novels with feminist and theosophist concepts in conversation with his mother-in-law, the suffragette Matilda Joslyn Gage. According to Wagner, Baum modeled Oz off of the prehistoric feminist utopia described in Gage’s 1893 Woman, Church and State. Wagner writes, “Gage described a period of matriarchy in the world’s history before private property, industrialization, and organized religion introduced inequality, greed, and genocide. The female principle—the creative principle—was held sacred and supreme, and cooperation, not competition, was the order of the day” (10). While the girls in Oz are traditionally feminine save only the Wicked Witches, they also dominate the land. By the time of The Emerald City, the most powerful individuals in Oz are Glinda, Ozma, and Dorothy, later joined by Trot in The Scarecrow of Oz. Even in the “uncivilized” Oz, men such as the Wizard and Omby Amby (the Soldier with the Green Whiskers) are ineffective, whereas Dorothy, the Wicked Witches, Jinjur, Mombi, and Glinda possess genuine cunning and power.

The Marvelous Land of Oz may appear to contradict the general feminism of the series. However, Wagner offers a feminist reading. The novel concerns a group of boys (Tip, Jack, the Sawhorse, the Scarecrow, the Tin Woodman, and the Woggle-Bug) who face the all-woman Army of Revolt, unserious and childish girls parodying suffragettes. The woman soldiers are frivolous and incompetent, and their leader, Jinjur, does not aim for gender equality but to rule over men, as in the ugliest anti-feminist caricature of the period. However, women are genuinely powerful. The male-dominated Oz is completely powerless and easily falls, and the Army of Revolt prove competent antagonists. When Tip and his group reach the Emerald City and find men engaged in wifely chores, the Scarecrow has this interaction with one of the exhausted husbands that highlights the value and difficulty of domestic labor:
“I’m glad you have decided to come back and restore order, for doing housework and minding children is wearing out the strength of every man in the Emerald City.”
“Hm!” said the Scarecrow, thoughtfully. “If it is such hard work as you say, how did the women manage it so easily?”
“I really do not know,” replied the man, with a deep sigh. “Perhaps the women are made of cast-iron.” (170–171)
Wagner takes this to mean that the men have a newfound appreciation for the value of feminine labor. Jinjur ultimately loses but not to any men, none of whom are capable of the task. Instead, Glinda defeats her with a different all-woman army. Unlike Jinjur’s comical soldiers who fight with knitting needles and want new jewelry, Baum treats Glinda’s militant women with relative respect and seriousness, demonstrating women can be effective. “[T]hese soldiers of the great Sorceress were entirely different from those of Jinjur’s Army of Revolt, although they were likewise girls. For Glinda’s soldiers wore neat uniforms and bore swords and spears; and they marched with a skill and precision that proved them well trained in the arts of war” (237).
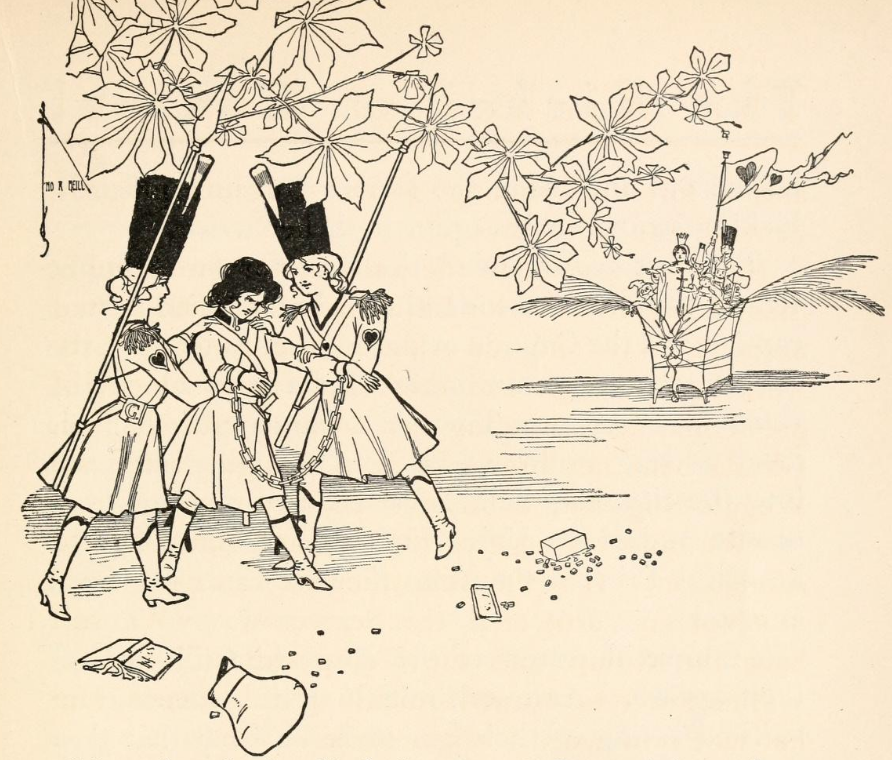
Furthermore, in the end, the boy hero Tip must become or even mature into a girl, Ozma, to prevail over Jinjur, though Wagner overstates when claiming the story “exposes the social construction of gender in all its complexity” (11). Jinjur’s childish scheme to invert gender roles fails, but a girl, Ozma, nonetheless ends up ruling with the authentic womanly power that Jinjur wants to see enthroned. The women also celebrate liberation from Jinjur (282–283). Instead of the supremacy of women, Ozma ensures equality.
The ascendancy of kind women instead of conquering Wicked Witches and a false Wizard is pivotal to the civilizing of Oz. It is Ozma’s gender equality and feminine power that changes the bleak albeit colorful land into a utopia. Later injustices are also corrected through the elevation of women and the removal of power from ill-intentioned men. In The Scarecrow of Oz, the Scarecrow, acting on behalf of the female Glinda, deposes Jinxland’s wicked King Krewl, a man, and Gloria, a woman, ascends the throne, ensuring peace and justice. Oz is a feminist utopia, particularly by the standards of the early twentieth century, when women in most of the United States were legally barred from even voting.