Finally, Oz indeed respects difference, likely at least part of the reason for its lasting appeal among queer audiences, as Dee Michel describes in “Not in Kansas Anymore: The Appeal of Oz for Gay Males.” Michel primarily focuses on the MGM adaptation of The Wonderful Wizard of Oz, but he does not neglect the novels. In particular, he notes the presence of non-traditionally masculine men such as the compassionate, tearful dandy the Tin Woodman or the Cowardly Lion, a “sissy” who wears a bow in his mane: “they are about as un-macho as one can get and still be recognizably male” (Michel 34).
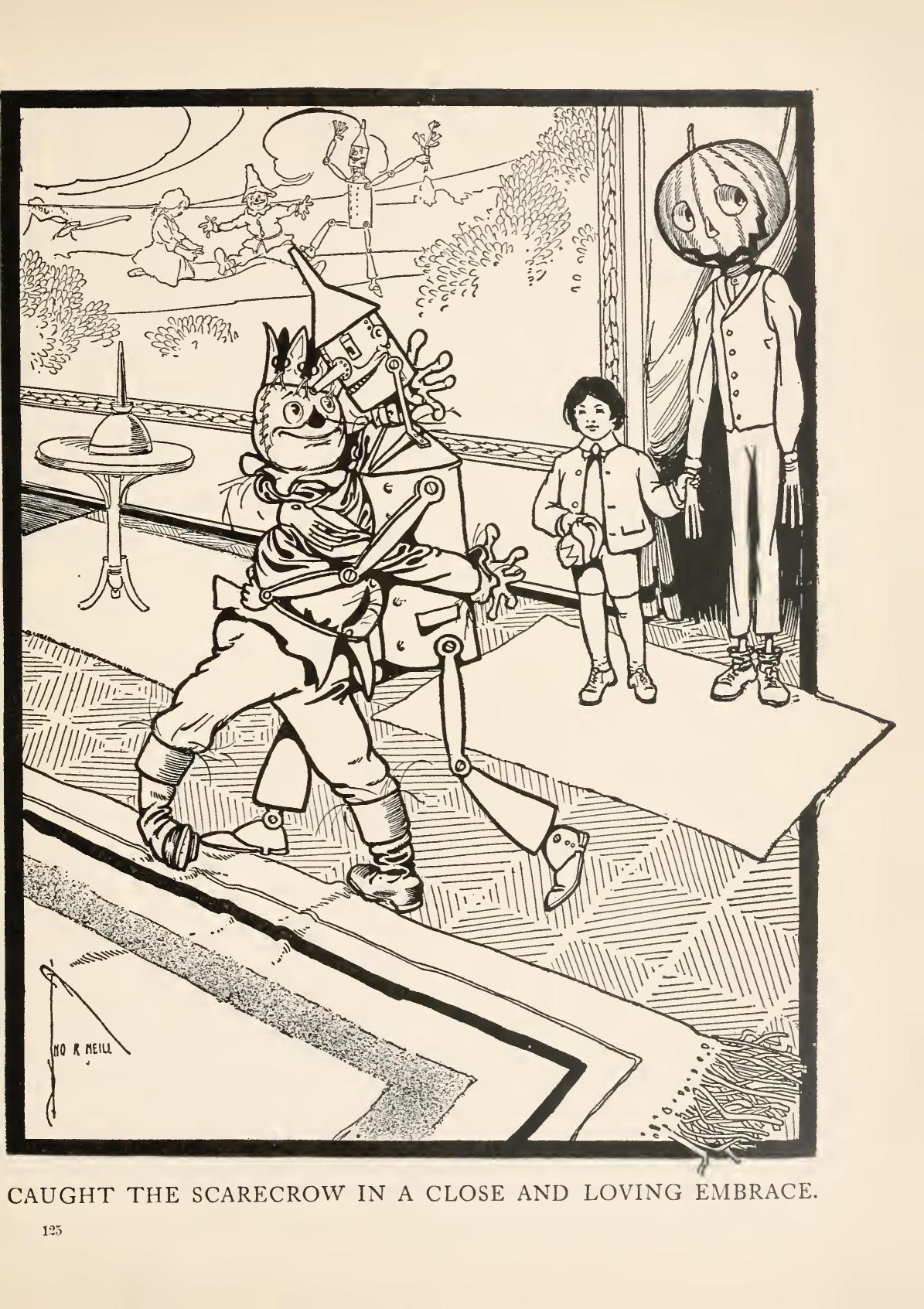

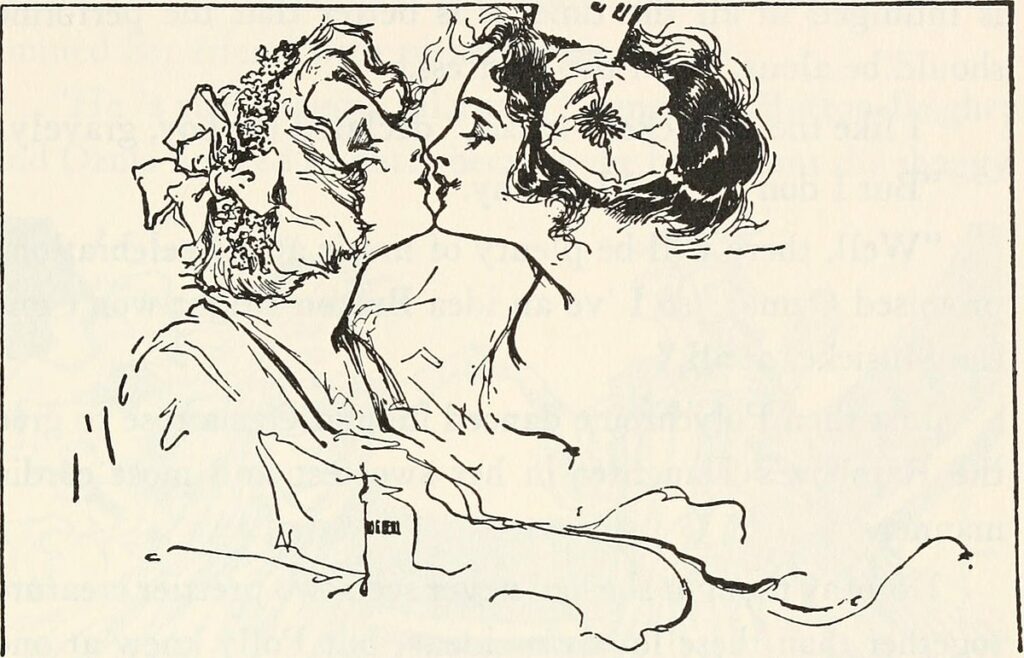
While Michel mentions the high level of physical affection present between the Scarecrow and the Tin Woodman, he neglects to note more overtly queer themes present in Baum’s text. Ozma is often read as transgender: seemingly a boy, she is a girl whose true nature the “uncivilized” version of Oz conceals from her until she succeeds in becoming her authentic self. Ozma and Dorothy’s mutual affection may appear to extend beyond what modern readers would take as just friendship. The two hug, smooch, and hold hands; live together; never show any romantic interest in any boys; and appear kissing each other on the lips in at least two of John R. Neill’s illustrations. Chick, originally appearing in John Dough and the Cherub before meeting Dorothy in The Road to Oz, is gender ambiguous or nonbinary, rejecting both boyhood and girlhood. Scraps reads as a queer allegory. “I must be the supreme freak. […] But I’m glad—I’m awfully glad!—that I’m just what I am, and nothing else” (Patchwork Girl 57). She rejects the birth name her oppressive parents Margolotte and Pipt intend for her, defiantly and joyfully embraces her unconventional identity, and rejects conservative gender roles in the country of the Horners.
“You have some queer friends, Dorothy,” [Polychrome] said.
“The queerness doesn’t matter, so long as they’re friends,” was the answer (Road 184).
Queerness, then, is welcome in Oz—especially uncommon given that Baum wrote them from 1900 to 1919. Michel proceeds to observe that diversity is a key value of Oz and quotes other writers on the subject:
Willard Carroll notes that “[Oz is] a community that celebrates the ultimate in creativity and diversity.” Similarly, Suzanne Rahn observes that “the characters themselves…are…fiercely tolerant of the outlandish, respecting, cherishing such rickety, sagging, unlikely colleagues as the Frogman, the Shaggy Man and Prof. H. M. Wogglebug, T.E.—a community of eccentrics. In Oz, they belong” (34).
Michel states, “All minorities would likely find Oz’s diversity compelling” (36). Put a pin in that. In addition to social outcasts, however, Baum treats Oz specifically as offering freedom from the capitalism of “the big, cold, outside world” in both The Road to Oz and The Emerald City. The former involves an American vagrant, the Shaggy Man, who “[has] slept more in hay-lofts and stables than in comfortable rooms” (196). In the mundane US, he is shunned and disliked, presumably for his frightening appearance and poverty. He steals the magical Love Magnet to force people to like him: “no one loved me, or cared for me, […] and I wanted to be loved a great deal” (208). The “big, cold, outside world” forces him to commit crime to have any hope of receiving love. However, in Oz, Shaggy is astonished to be welcomed into palaces and receive the treatment of a royal, for Oz “[has] no rich, and no poor” (165) and the people value only love, not money. So he chooses to remain there, though continues to wander the land for fun.

Similarly, in The Emerald City, Dorothy’s Uncle Henry and Aunt Em receive liberation from their poverty and debt in Kansas by moving to Oz. Baum depicts US life as brutal and withering. In The Wonderful Wizard, Dorothy, Henry, and Em inhabit a one-room shack. Henry “[works] hard from morning till night and [does] not know what joy [is]” (13). This life literally removes hope and happiness from Em: “[The sun and wind] had taken the sparkle from her eyes and left them a sober gray […] She was thin and gaunt, and never smiled, now” (12). After the cyclone destroys the house, Henry builds a new one, yet his health declines until he can no longer work. With the mortgage unpaid, the family is doomed to lose their home. In Oz, however, Henry and Em are overwhelmed with gold and gems and dressed in regal Munchkin clothing, with merry servants sparing them from ever working again.
“I’ve been a slave all my life,” Aunt Em replied, with considerable cheerfulness, “and so was Henry. I guess we won’t go back to Kansas, anyway” (269–270).
Slavery and freedom are major preoccupations throughout the series. The chief crime of the Wicked Witches, Nomes, Queen Cor and King Gos, and other powerful antagonists is the enslavement of others. Given the Em’s above comment, then, life in the economic conditions of the ordinary world is tantamount to slavery. The assorted evil forces outside of Oz correspond to the mundane violence of real societies, as Jack Zipes observes: “Baum draws a parallel between the bankers, who are merciless and crush old farmers who can no longer be employed because of bad health, and the Nome King and his allies, the Whimsies, Growleywogs, and Phanfasms, who want to enslave people to attain wealth and power.” Recall that Vidal similarly takes the Nome King to suggest the prevailing economic order of the US.